Olympus mons is a very large volcano on planet March and it may be the largest volcano in our solar system. This giant Martian peak, which was photographed by Mariner 9 which orbited the planet March during 1971 and 1972 ,The olympus mons rises almost 22 kilometers(13.6 miles or 72,000 ft) high and measures 550 km across. By comparison, Earth's largest volcano, Mauna Loa in Hawaii, rises 4,169 meter(13,678 ft) above sea level and measures 120 km across. Such large volcanoes can exist on Mars because of the low gravity and lack of surface tectonic motion. Olympus Mons is a shield volcano.A shield volcano is a type of volcano usually built almost entirely of fluid lava flows. They are named for their low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. This is caused by the highly fluid (low viscosity) lava they erupt which travels farther than lava erupted from stratovolcanoes. This results in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form. The shape of shield volcanoes is due to the low viscosity of their mafic lava.
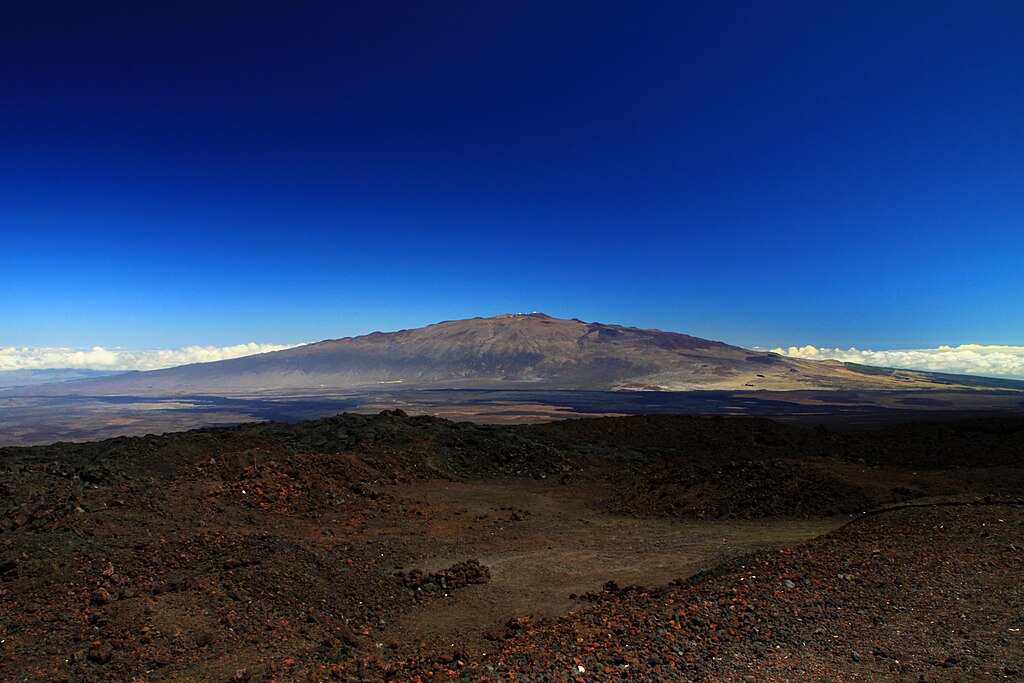 |
| Mauna Kea, Hawaiʻi, a shield volcano on the Big Island of Hawaii |
The volcano is located in Mars's western hemisphere at approximately 18.65°N 226.2°E, just off the northwestern edge of the Tharsis bulge. The western portion of the volcano lies in the Amazonis quadrangle (MC-8) and the central and eastern portions in the adjoining Tharsis quadrangle (MC-9).
Olympus Mons is still a relatively young volcano. Although it has taken billions of years to form, some regions of the mountain may be only a few million years old, relatively young in the lifetime of the solar system. As such, Olympus Mons may still be an active volcano with the potential to erupt.
DESCRIPTION:
The typical atmospheric pressure at the top of Olympus Mons is 72 pascals, about 12% of the average Martian surface pressure of 600 pascals. Both are exceedingly low by terrestrial standards. By comparison, the atmospheric pressure at the summit of Mount Everest is 32,000 pascals, or about 32% of Earth's sea level pressure. Olympus Mons shows that there is a composition of 44% silicates, 17.5% iron oxides, giving the planet its red coloration, 7% aluminum, 6% magnesium, 6% calcium, and particularly high proportions of sulfur oxide with 7%. These results point to the fact that the surface is largely composed of basalts and other mafic rocks, which would have erupted as low viscosity lava flows and hence lead to the low gradients on the surface of the planet. After plate tectonics ceased on Mars, hotspots, which cause volcanoes such as these, remained under the same areas for a very long time, and the volcanoes kept growing. Olympus Mons is supported by a 70 km (43 mi) thick lithosphere.
 |
| Vertical comparison of Olympus Mons with Mount Everest (shown sea-level-to-peak) and Mauna Kea on Earth |

Another reason of existence of this kind of giant volcanoes on march is because the crust on march doesnot move like the crust on planet earth. On earth the ,the hot spots remain stationary but the crustal plates are moving above them .The Hawaiian island result from the northwesterly movement of pacific plate over a stationary hotspot producing lava. As the plate moves over the hotspot, new volcanoes are formed and the existing ones become extinct.This distributes the total volume of lava among many volcanoes rather than one large volcano. On march the crust remains stationary and the lava piles up in one ,very large volcano.
Mt. Everest might be the tallest mountain on the earth, but it is nothing in compared to the olympus mons on our nearest red planet or March.The olympus mons is almost three times that the height of the Mt. Everest. Scientist estimate that this giant volcano last time erupted lava onto the martian surface was between 20-200m million years ago,around the same that dinosaurs ruled on our planet.While some scientist that this last eruption on olympus mons marks the last breath of volcanic activity on march , Others suggest this monstrous volcano is still active despite being dormant for millions of years.
THANKS FOR READING.
Reference:wikipedia
image credit:nasa