The solar wind is a stream of charged particles, primarily electrons and protons, emitted by the sun(star) which penetrate the solar system at speeds as high as 300-800km/s.This type of emitting charged particles which are released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona.In 1859, it was first suggested by British astronomer Richard C. Carrington.
It was not until 1962 that solar wind was proved to exist. The spacecraft Mariner II directly detected the solar wind on its way to Venus.

The Wind spacecraft has spent much of its 20 years in space out in front of the magnetic fields – the magnetosphere – that surrounds Earth, observing the constant stream of particles flowing by from the solar wind.
IMAGE CREDIT:NASA
The process in which two light nuclei combine (at extremely high temperature)to form a single heavier nucleus is called nuclear fusion.Fusion is the source of energy in sun and stars . The sun has been radiating energy at the rate of 3.8✖ 10^26 J/S for several billion years without showing any sign of cooling off. A satisfactory explanation for this phenomenon was given by H. Bethe in 1939. hydrogen nuclei ,i.e protons are most abundant in the body of sun and stars . At extremely high temperature which exits in interior of the sun and stars ,protons fuse together to form helium nuclei ,liberating a huge amount of energy.
The solar wind refers to the steady stream of highly charged particles that continually blow of the sun in all direction. The corona which is outer atmosphere of the sun expanding into the space and caused this.You can see it as a glowing halo around the sun during a solar eclipse.
Hydrogen atoms heat up to more than 1 million °C on the solar surface, then decompose into electron and protons.They are called plasmas. The plasma gas is forced to burst out from the solar surface by the high pressure it has.The plasma gas then runs through interplanetary space at ultra-high-speed as fast as 300-800 km per second!That is the solar wind.
The slow solar wind appears to originate from a region around the Sun's equatorial belt that is known as the "streamer belt", The exact coronal structures involved in slow solar wind formation and the method by which the material is released is still under debate.
Average solar wind parameters at 1 AU, for the time around solar activity minimum.
slow wind fast wind
Flow speed 300–500 km s−1 500–800 km s−1
Proton flux density 3.7 × 10^8 cm−2 s−1 2.0 × 10^8 cm−2 s−1
Proton temperature 3.4 × 10^4 K 2.3 × 10^5 K
Electron temperature 1.3 × 10^5 K 1 × 10^5 K
Momentum flux density 2.12 × 10^8 dyn cm−2 2.26 × 10^8 dyn cm−2
Total energy flux density 1.55 erg cm−2 s−1 1.43 erg cm−2 s−1
Helium content 2.5%, variable 3.6%, stationary
Sources Streamer belt Coronal holes


Sunspot are temporary phenomena on the sun’s surface that appear visibly as dark spots compared to surrounding regions.
The
red and blue arrows indicate solar wind speed; longer arrow represents higher
speeds.
🗙Solar minimum, when
sunspots are rare.
🗙Solar
maximum, when
the Sun is very active and sunspots are common.Sunspot are temporary phenomena on the sun’s surface that appear visibly as dark spots compared to surrounding regions.

A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant release of plasma and magnetic field from the solar corona. They often follow solar flares and are normally present during a solar prominence eruption. The plasma is released into the solar wind.Coronal mass ejections are often associated with other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accepted theoretical understanding of these relationships has not been established. CMEs most often originate from active regions on the Sun's surface, such as groupings of sunspots associated with frequent flares. Near solar maxima, the Sun produces about three CMEs every day, whereas near solar minima, there is about one CME every five days.
It affects it by the intense clouds of high energy particles that it often contains which are produced by solar storms. When these clouds, called coronal mass ejections, make their way to the Earth, they collide with the magnetic field of the Earth and cause it to change its shape.
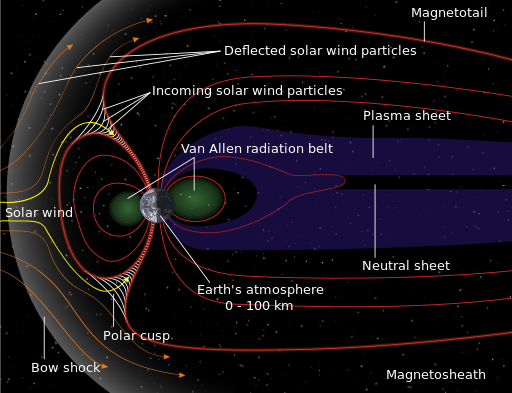
 As you have already learned, the Earth is also a huge magnet with north and south poles.The geomagnetic field lines are blocking the solar wind like a barrier. This barrier, however, cannot entirely shield the solar wind.When the solar wind buffets the geomagnetic field, its huge energy penetrates into the Earth‛s magnetosphere in various forms.The particles then leak through the magnetic field of the Earth, particularly near the north and south poles, and cause still more changes to the magnetic field of the Earth, this time at even lower altitudes closer to the ground. These changes can produce many problems with electrical equipment.
As you have already learned, the Earth is also a huge magnet with north and south poles.The geomagnetic field lines are blocking the solar wind like a barrier. This barrier, however, cannot entirely shield the solar wind.When the solar wind buffets the geomagnetic field, its huge energy penetrates into the Earth‛s magnetosphere in various forms.The particles then leak through the magnetic field of the Earth, particularly near the north and south poles, and cause still more changes to the magnetic field of the Earth, this time at even lower altitudes closer to the ground. These changes can produce many problems with electrical equipment.
Aurora

 Auroras are produced when the magnetosphere is sufficiently disturbed by the solar wind that the trajectories of charged particles in both solar wind and magnetospheric plasma, mainly in the form of electrons and protons, precipitate them into the upper atmosphere (thermosphere/exosphere) due to Earth's magnetic field, where their energy is lost.The solar wind, the flow of plasmas, creates the aurora by colliding with the atoms and molecules of the Earth‛s upper atmosphere.
Auroras are produced when the magnetosphere is sufficiently disturbed by the solar wind that the trajectories of charged particles in both solar wind and magnetospheric plasma, mainly in the form of electrons and protons, precipitate them into the upper atmosphere (thermosphere/exosphere) due to Earth's magnetic field, where their energy is lost.The solar wind, the flow of plasmas, creates the aurora by colliding with the atoms and molecules of the Earth‛s upper atmosphere.
Cosmic rays are traveling from far away in space. They are high energy particles and are harmful to life on the ground, if they hit the Earth directly.Now, the solar wind with magnetic fields plays a role as a barrier to protect the Earth from being directly hit by cosmic rays! We can say that life is shielded by the magnetized solar wind. the Sun is blasting out 1 million tons of solar wind every second.The Sun loses a mass of 30 trillion tons per year in the form of solar wind.In the meantime, the total mass of the Sun is 30 trillion multiplied by 70 trillions.Simply calculating, it takes 70 trillion years for the Sun to lose its whole mass.
INFLUENCE OF THE SOLAR WIND ON EARTH
The solar wind has a significant influence on our ionosphere, the Earth’s magnetic field, on earth’s Aurora, and on telecommunication systems.
HOW DOES SOLAR WIND AFFECT HUMAN HEALTH
There is an increased cancer risk for astronauts in space, who are hit by the particles of the solar wind, and there may similarly be an increased risk of cancer, or cell damage to humans located at the magnetic poles. (e.g. people gathered to watch the Auroras)
It affects it by the intense clouds of high energy particles that it often contains which are produced by solar storms. When these clouds, called coronal mass ejections, make their way to the Earth, they collide with the magnetic field of the Earth and cause it to change its shape.
Aurora
Aurora is one of the phenomena caused by the energy from the Sun! An aurora (plural: auroras),sometimes referred to as polar lights, northern lights (aurora borealis) or southern lights (aurora australis), is a natural light display in the Earth's sky, predominantly seen in the high latitude (Arctic and Antarctic) regions.
Cosmic rays are traveling from far away in space. They are high energy particles and are harmful to life on the ground, if they hit the Earth directly.Now, the solar wind with magnetic fields plays a role as a barrier to protect the Earth from being directly hit by cosmic rays! We can say that life is shielded by the magnetized solar wind. the Sun is blasting out 1 million tons of solar wind every second.The Sun loses a mass of 30 trillion tons per year in the form of solar wind.In the meantime, the total mass of the Sun is 30 trillion multiplied by 70 trillions.Simply calculating, it takes 70 trillion years for the Sun to lose its whole mass.
INFLUENCE OF THE SOLAR WIND ON EARTH
The solar wind has a significant influence on our ionosphere, the Earth’s magnetic field, on earth’s Aurora, and on telecommunication systems.
There is an increased cancer risk for astronauts in space, who are hit by the particles of the solar wind, and there may similarly be an increased risk of cancer, or cell damage to humans located at the magnetic poles. (e.g. people gathered to watch the Auroras)
WHY DO WE STUDY THE SOLAR WIND?
The solar wind is an important research topic.
There are a large number of phenomena, which we don’t or only partially understand.
One hopes that a better understanding of the solar wind will give us insight in the behavior of stars.
thanks for reading.
reference :wiki


No comments:
Post a Comment